Ra: Unveiling The Secrets Of The Egyptian Sun God
Who was Ra, the sun-drenched deity at the heart of ancient Egyptian civilization? Ra wasn't just a god; he was the very essence of creation, the life-giving force that shaped the world and dictated the rhythm of existence for an entire civilization.
The ancient Egyptians, a people steeped in a profound connection to the cosmos, looked to the heavens for understanding, guidance, and sustenance. At the center of their elaborate pantheon stood Ra, the sun god, a figure of unparalleled importance and reverence. His influence permeated every facet of Egyptian life, from the grandest religious ceremonies to the most intimate daily rituals. Ra's dominion wasn't limited to the visible; he ruled over the sky, the earth, and even the mysterious underworld, making him a truly omnipresent deity.
Here's a glimpse into the multifaceted world of Ra, the sun god of ancient Egypt:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Ra (also Re) |
| Role | God of the Sun, Creation, Life, and Order |
| Domain | Sky, Earth, Underworld |
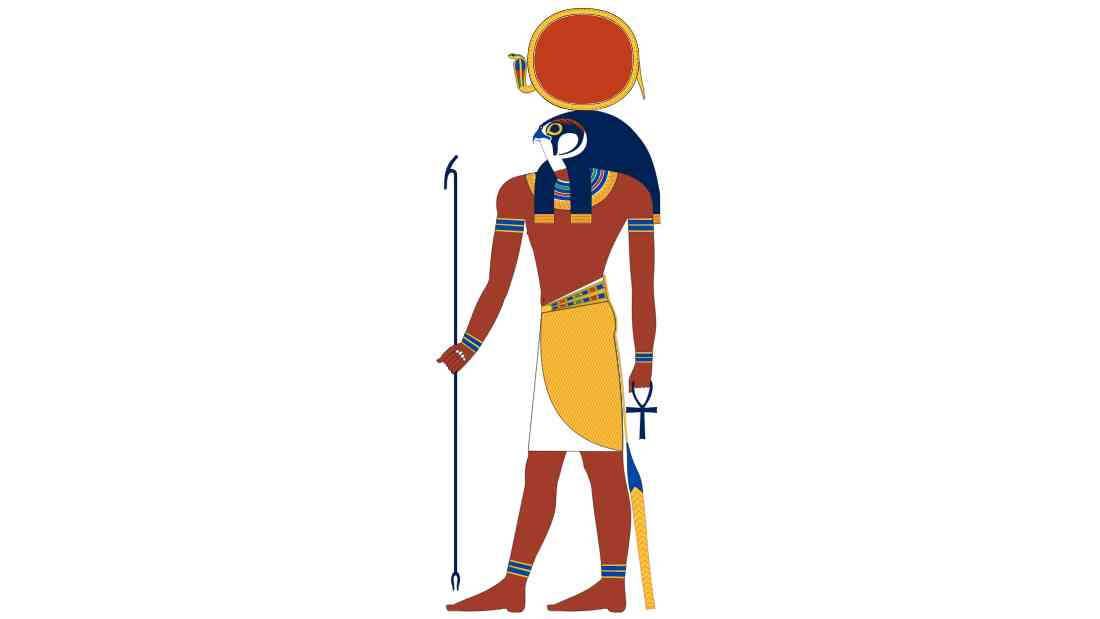
| Symbol | Sun Disk, Falcon, Ankh |
| Family | Father of all other Egyptian Gods (often associated with the Ennead) |
| Worship | Prominent from the 5th Dynasty onward; considered the chief deity |
| Mythology | Creator of the world and humanity (from sweat and tears); daily journey across the sky; associated with kingship. |
| Depiction | Often depicted with the head of a falcon wearing a sun disk |
| Significance | Central to Egyptian religion and mythology, representing life, light, and the cycle of rebirth. |
| Associated Deities | Horus, Amun (through merging), Aten |
Reference: Britannica - Ra, Egyptian god
Ra's reign wasn't confined to the temporal; he held sway over the very fabric of existence. He was the architect of creation, the one who breathed life into the world and set the celestial bodies in motion. The ancient Egyptians believed Ra ruled not only the sky and the earth, but also the underworld, illustrating his comprehensive control over every aspect of their world. He was also considered the first pharaoh of ancient Egypt, solidifying his status as a divine ruler and the ultimate source of authority.
Ra's appearance in ancient Egyptian art is a testament to his significance. Often, he's portrayed with the head of a falcon, a symbol of divine kingship and soaring power. Perched atop his head is the radiant sun disk, a visual representation of his celestial domain and life-giving energy. The ankh, the symbol of life, is frequently associated with him, further emphasizing his role as the creator and sustainer of all living things.
Ra's story is intertwined with the daily cycle of the sun. Each morning, he was believed to be reborn, his journey across the sky representing the eternal cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. At night, he would travel through the perilous underworld, battling the forces of chaos before triumphantly emerging again at dawn. This daily journey was a powerful metaphor for the human experience, a reminder of the constant renewal and the promise of overcoming adversity.
Ra's influence extended beyond the purely mythological. Kings, or pharaohs, often claimed descent from Ra, solidifying their claim to power and linking themselves to the divine. Heliopolis, the "City of the Sun," served as his primary cult center, where elaborate rituals and ceremonies were performed to honor him. The worship of Ra, which rose to prominence during the Fifth Dynasty (25th and 24th centuries BC), continued to be a central aspect of Egyptian religious life for centuries.
Ra's role as the creator god also linked him to the Ennead, a group of nine of the most important gods and goddesses in the Egyptian pantheon. This association further solidified his position as the father of all the other deities, the source from which all divine power originated. The concept of Ra as the sun god of Heliopolis, the birthplace of the gods, makes him a fundamental component of Egyptian cosmology.
Over time, Ra's identity merged with that of other gods, such as Horus (the falcon-headed god often associated with kingship) and Amun (a powerful god associated with the wind and the hidden aspects of the universe). These mergers reflected the evolving religious beliefs of the Egyptians and underscored the interconnectedness of the divine. The fusion of Ra and Amun resulted in Amun-Ra, a deity considered the most powerful of all Egyptian gods.
The Eye of Ra is another critical facet of his persona. This symbol represented the sun's intense heat and life-giving energy and also held aspects of divine protection and retribution. The myths regarding the Eye of Ra are numerous, however, one of the most popular is the narrative of the fierce lioness, Sekhmet, often seen as the Eye of Ra, nearly destroying humanity before being pacified with beer. The Eye of Ra symbolizes his power and his vigilant care over the world.
Ras influence wasnt constant throughout Egyptian history. The worship of Aten, the sun disk, briefly replaced the worship of Ra during the reign of Akhenaten (Amenhotep IV), who established a new religious system called Atenism. However, after Akhenaten's reign, the worship of Ra was restored to its former glory.
The sun, central to life in the desert climate of Egypt, naturally led to Ra becoming the creator of life. Ra was responsible for providing the warmth, light, and the growing seasons necessary for the prosperity of Egypt. This is why Ra was seen as king. His journey each day across the sky, symbolized the rhythm of existence, embodying the eternal promise of renewal.
Understanding Ra is key to understanding ancient Egyptian civilization. He was more than a deity; he was a symbol of life, creation, and the very essence of Egyptian identity. His enduring legacy, reflected in art, mythology, and religious practices, continues to captivate and inspire, providing a window into the rich and complex world of the ancient Egyptians.